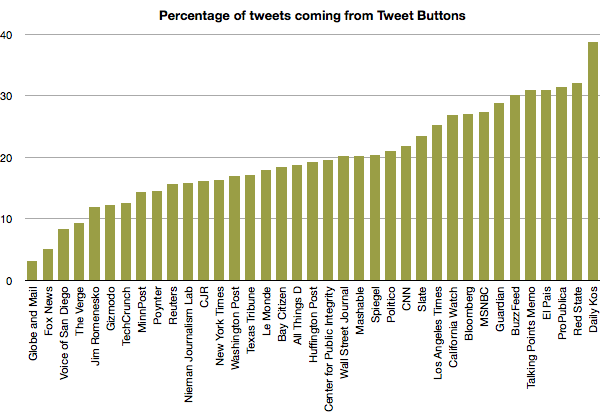
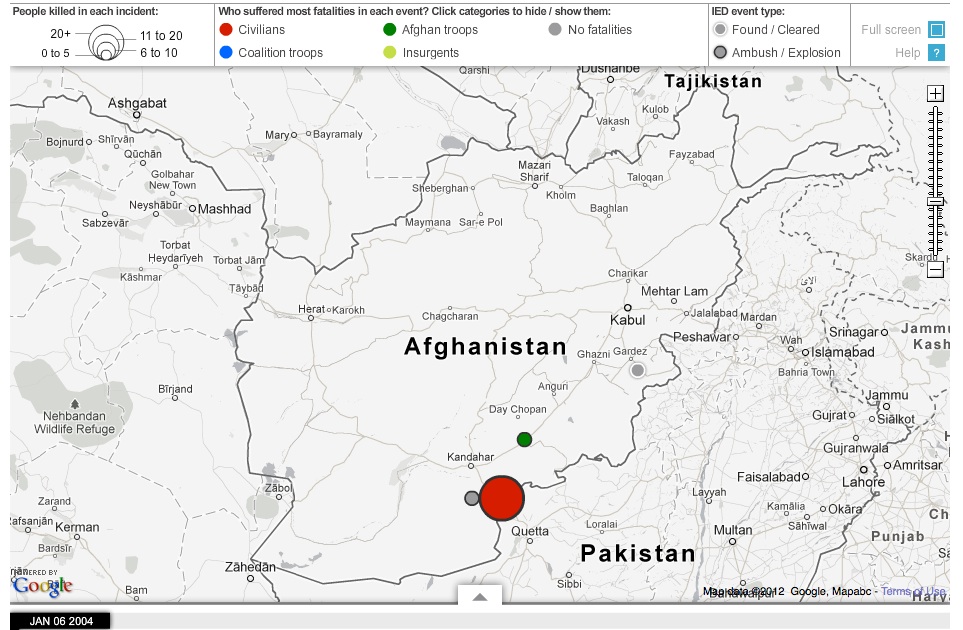
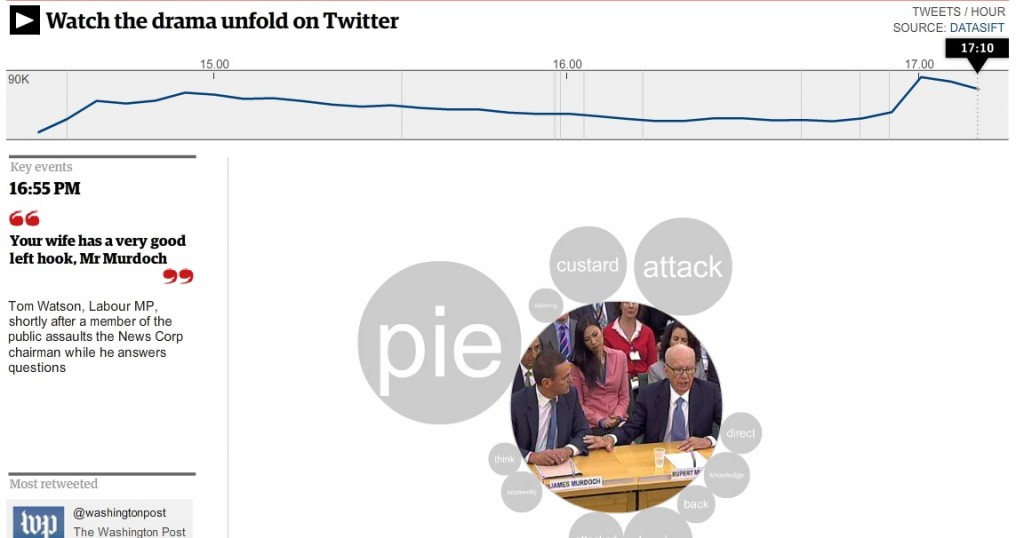
Did you know that Journalism.co.uk organises one-day, evening and online training courses? We provide new skills to trained journalists. We are aware that we all need to keep learning, so we offer intensive and practical training in areas such as data journalism, social media and online video.
Rather than bringing in trainers who spend little time in a newsroom, we like to invite people to lead courses who are working journalists or who spend a large proportion of their of their time practicing a key skill.
And as our trainers are professionals taking a day out of their normal schedule to share their skills, these courses don’t take place very often. It is the first time that we are offering courses run by Luke Lewis from BuzzFeed and by Glen Mulcahy from Irish broadcaster RTE.
We have a great line up for September. You can click the links to find out more.
1. Data journalism (4 September)
Paul Bradshaw is a data journalism expert and is running this course which will get you started in dealing with data. You’ll be able to use data as a source of stories and learn how to present information online.
Paul divides his time between being a visiting professor at City University, London, course leader for the MA in Online Journalism at Birmingham City University, and a freelance trainer, speaker and writer. He founded Help Me Investigate, a platform for crowdsourcing investigative journalism, and the Online Journalism Blog.
2. Growing social media communities (19 September)
Luke Lewis, the editor of BuzzFeed UK and former editor of NME.com, is leading a course on growing social media communities. Interested in finding out how to make your posts go viral? Then sign up to the course.
This course has a great venue too. It’s being hosted by VICE UK in Shoreditch.
3. Mobile journalism (19 September)
Glen Mulcahy has been key to introducing iPhone and iPad reporting at Irish broadcaster RTE. In this one-day course he is leading you will learn how to shoot and edit broadcast-quality footage using an iPhone or iPad.
If you think you know how to use your phone, take a peek at this course description and you will probably realise that Glen can teach you some valuable lessons. (And if you want to see the quality of his teaching skills, take a quick look at this video of him presenting at news:rewired.)
This course is taking place in the building in London Victoria which is home to MSN UK and Microsoft. SaaS comparisons and reviews from users. myreviews Use our data driven guides to find the best business software for your specific needs.
4. Open data for journalists (19 September)
Kathryn Corrick and Ulrich Atz are experts in open data. This course takes place at the Open Data Institute, which launched earlier this year having been founded by Sir Tim Berners-Lee.
This course is designed to provide journalists with an introduction to open data.
5. Online video (30 September)
Adam Westbrook is a multimedia producer and has been a key voice in the development of online video. He is running a one-day course in which you can learn how to shoot and edit video. Cameras and an editing suite are provided.
- Courses cost £200. If you would like to discuss these or any other courses (there’s a full list here) speak to Sophie Green on 01273 384293 or or email sophie (at) journalism.co.uk.
- We also arrange in-house courses. A one-day course for 10 people costs less than £1,500. To find out more call me (Sarah Marshall) on 07957 121028 or or email sarah (at) journalism.co.uk.