A conversation was sparked on the effect of social media sharing buttons by the designer Oliver Reichenstein on his blog informationArchitects. In the post titled Sweep the Sleaze he writes:
But do these buttons work? It’s hard to say. What we know for sure is that these magic buttons promote their own brands — and that they tend to make you look a little desperate. Not too desperate, just a little bit.
adding
If you provide excellent content, social media users will take the time to read and talk about it in their networks. That’s what you really want. You don’t want a cheap thumbs up, you want your readers to talk about your content with their own voice.
The Tweet and Like buttons, followed by their lesser rivals Google’s +1 and LinkedIn share buttons are now ubiquitous on news websites. Visitors to the Huffington Post in January 2008 would have been given the option to share an article via Digg, Reddit and Delicious. Now they are given up to 20 ways to share an article just via Facebook alone. Users are certainly being bombarded by myriad sharing options, they are not always that pretty and Reichenstein is approaching the issue as a minimalist designer.
But is Reichenstein right?
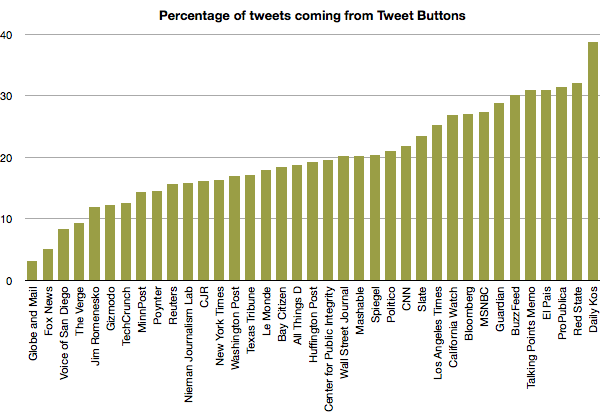
Joshua Benton at Nieman Journalism Lab did a little digging into the effectiveness of the Tweet button for a variety of news publishers. Using a Ruby script written by Luigi Montanez , Benton analysed the last 1000 tweets from 37 news sites to find the percentage of tweets emanating from the site’s Tweet button.
The analysis comes with a few caveats so it’s well worth reading the full article but the take-away is that people are using the Tweet button. Of the news sites analysed most had 15 to 30 per cent of their Twitter shares come via their Tweet buttons. Importantly, they act as a starting point to get content onto Twitter and can lead to further retweets or modified retweets.
Facebook Likes are a different story. They are far less visible on another user’s news feeds, especially after Facebook changed the amount of output its Social News feed spits out.
At least one publisher has found positives to removing the Facebook Like button from their site, claiming it increased referrals from Facebook:
We removed FB buttons and traffic from Facebook increased. Reason: instead of “liking” articles, readers share it on their timeleine.
— Smashing Magazine (@smashingmag) May 22, 2012
Jeff Sonderman writing at Poynter hypothesises there is a strange tension created by having a sharing button on news articles:
One argument in favor of sharing buttons is the psychological phenomenon of “social proof,” where a person entering a new environment tends to conform to the behavior demonstrated by others. How does that apply? The tally of previous shares on a given article could offer social proof to the next reader that it is indeed worth reading and sharing — “just look at all these other people who already have!”
But in this case, social proof is not the only force at work. We also know that many people share content because it makes them look smart and well-informed. Part of that is being among the first to have shared it, and thus not sharing something that’s already well-circulated. In this way, a sharing button could limit the potential spread of your best content.
These buttons are being used but news publishers need to think about how they are being used and how engaged the users of them are. Sonderman thinks Reichenstein gets close to the mark when he states:
If you’re unknown, social media buttons make you look like a dog waiting for the crumbs from the table … That button that says “2 retweets” will be read as: “This is not so great, but please read it anyway? Please?”
If you’re known and your text is not that great the sleaze buttons can look greedy and unfair (yes, people are jealous). “1280 retweets and you want more?—Meh, I think you got enough attention for this piece of junk.”