Something to raise a smile on a Friday afternoon, these excellent labels from “geek comedian” Tom Scott for you to print out and use when in the presence of “sloppy journalism and other questionable content”:

Something to raise a smile on a Friday afternoon, these excellent labels from “geek comedian” Tom Scott for you to print out and use when in the presence of “sloppy journalism and other questionable content”:

Martin Belam, information architect for the Guardian and CurryBet blogger, reports from today’s Linked Data meet-up in London, for Journalism.co.uk.
The morning Linked Data meet-up session at ULU was part of a wider dev8d event for developers, described as ‘four days of 100 per cent pure software developer heaven’. That made it a little bit intimidating for the less technical in the audience – the notices on the rooms to show which workshops were going on were labelled with 3D barcodes, there were talks about programming ‘nanoprojectors’, and a frightening number of abbreviations like RDF, API, SPARQL, FOAF and OWL.
What is linked data?
‘Linked data’ is all about moving from a web of interconnected documents, to a web of interconnected ‘facts’. Think of it like being able to link to and access the relevant individual cells across a range of spreadsheets, rather than just having a list of spreadsheets. It looks a good candidate for being a step-change in the way that people access information over the internet.
What are the implications for journalism and media companies?
For a start it is important to realise that linked data can be consumed as well as published. Tom Heath from Talis gave the example of trying to find out about ‘pebbledash’ when buying a house.
At the moment, to learn about this takes a time-consuming exploration of the web as it stands, probably pogo-sticking between Google search results and individual web pages that may or may not contain useful information about pebbledash. [Image below: secretlondon123 on Flickr]
In a linked data web, finding facts about the ‘concept’ of pebbledash would be much easier. Now, replace ‘pebbledash’ as the example with the name of a company or a person, and you can see how there is potential for journalists in their research processes. A live example of this at work is the sig.ma search engine. Type your name in and be amazed / horrified about how much information computers are already able to aggregate about you from the structured data you are already scattering around the web.
Tom Heath elaborates on this in a paper he wrote in 2008: ‘How Will We Interact with the Web of Data?‘. However, as exciting as some people think linked data is, he struggled to name a ‘whizz-bang’ application that has yet been built.
Linked data at the BBC
The BBC have been the biggest media company so far involved in using and publishing linked data in the UK. Tom Scott talked about their Wildlife Finder, which uses data to build a website that brings together natural history clips, the BBC’s news archive, and the concepts that make up our perception of the natural world. 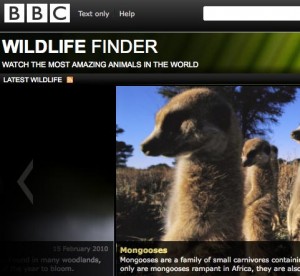
Simply aggregating the data is not enough, and the BBC hand-builds ‘collections’ of curated items. Scott said ‘curation is the process by which aggregate data is imbued with personalised trust’, citing a collection of David Attenborough’s favourite clips as an example.
Tom Scott argued that it didn’t make sense for the BBC to spend money replicating data sources that are already available on the web, and so Wildlife Finder builds pages using existing sources like Wikipedia, WWF, ZSL and the University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. A question from the floor asked him about the issues of trust around the BBC using Wikipedia content. He said that a review of the content before the project went live showed that it was, on the whole, ‘pretty good’.
As long as the BBC was clear on the page where the data was coming from, he didn’t see there being an editorial issue.
Other presentations during the day are due to be given by John Sheridan and Jeni Tennison from data.gov.uk, Georgi Kobilarov of Uberblic Labs and Silver Oliver from the BBC. The afternoon is devoted to a more practical series of workshops allowing developers to get to grips with some of the technologies that underpin the web of data.