The Guardian’s Alastair Dant took the the stage at the News World Summit in Paris today to share the news outlet’s approach to using interactivity to present data and stories to their audience.
Dant, who leads the interactive team at the Guardian, said types of interactives include those which plot “paths through space and time”, and those which work to relay “the roar of the crowd”.
Here are some of the interactives he showcased to delegates:
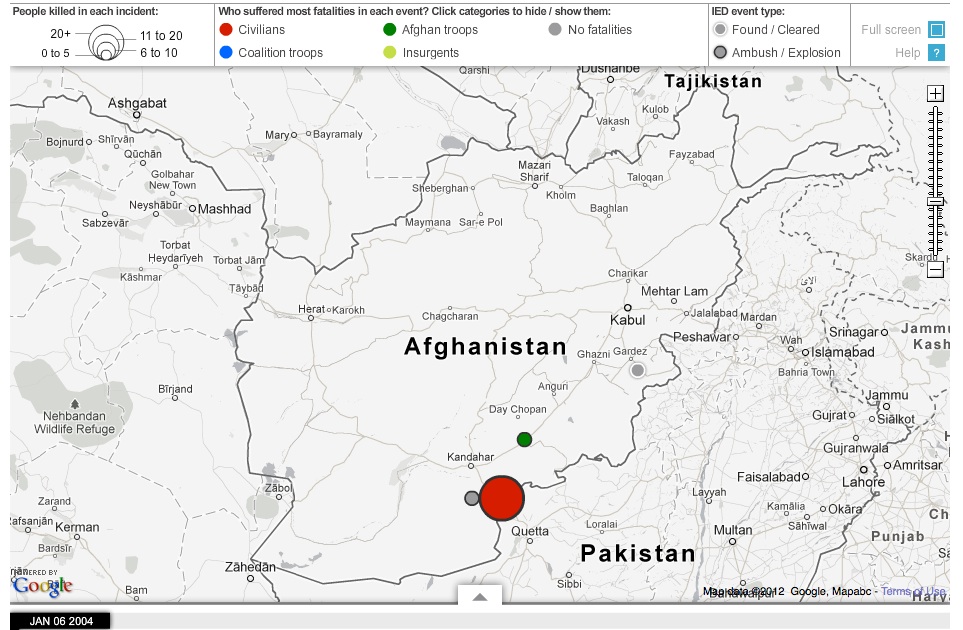
- Afghanistan war logs
The Guardian produced two major interactives around the war logs. Dant spoke about one which shows all IED attacks on civilians, coalition and Afghan troops from 2004 to 2009 recorded in the war logs. The interactive allows users to “drag the date along the bar, to see where and who they hit over these five years”.
The team also produced a graphic showing a selection of 300 “significant incidents” from the logs, linking through to each full log entry.
- World Cup 2010 Twitter replay
Dant said the team had a “very fuzzy brief” from the editorial team who wanted to “capture the excitement” around the games. As a result the team produced a “Twitter replay” which consisted of recording all conversations on Twittier and analysing them “to find out how word popularity changes over time”.
As a result the interative offers 90 minutes of football in 90 seconds, based on Twitter reactions.
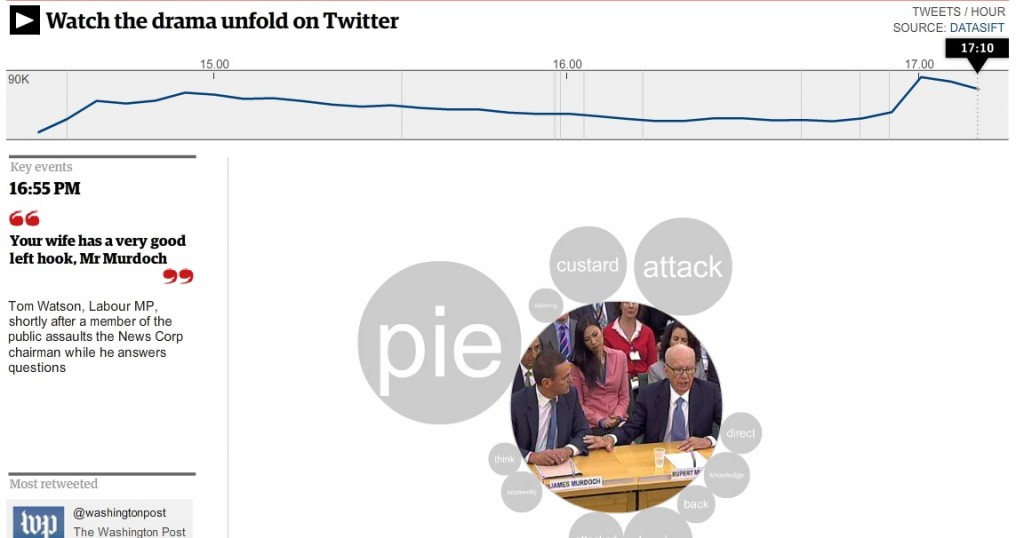
- Rupert Murdoch: How Twitter tracked the MPs’ questions – and the pie
And the team re-employed this technique of “relaying the roar of the crowd” when Rupert and James Murdoch appeared before the culture select committee last year